How does the ADHD brain differ from a regular brain? From brain scans to behavior, the distinctions are clear. This article delves into the ADHD brain vs normal brain scan, its dopamine levels, developmental age, and even compares it to autistic brains. Let’s explore the seven key differences to better understand ADHD and its impact on both children and adults.
The Neurochemical Difference: Dopamine’s Role
1. ADHD Brain vs. Normal Brain: A Dopamine Dilemma
One of the primary differences between ADHD and non-ADHD-brains lies in the neurotransmitter dopamine. Dopamine plays a crucial role in motivation, attention, and reward processing. Individuals with ADHD often have lower levels of dopamine or reduced sensitivity to its effects. This can lead to difficulty focusing, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. For those wondering how to read with ADHD, strategies like breaking reading into smaller chunks, using a timer, or incorporating active reading techniques can help maintain focus and engagement.
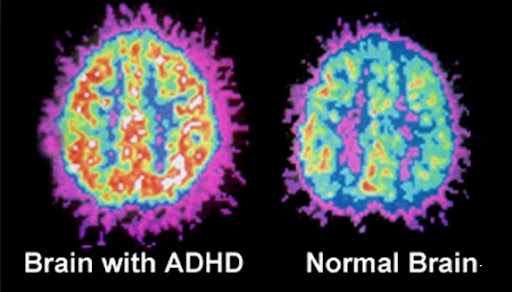
2. Structural Differences in the Brain:
ADHD Brain vs. Normal Brain: A Structural Perspective
Neuroimaging studies have revealed structural differences between the brains of individuals with and without ADHD. Key areas affected include:
- Prefrontal Cortex: Responsible for executive functions like planning, decision-making, and impulse control.
- Basal Ganglia: Involved in movement, reward processing, and habit formation.
- Cerebellum: Plays a role in motor control, balance, and cognitive functions.
People with ADHD may have smaller volumes in these brain regions, which can contribute to their challenges with attention, focus, and impulse control.
3. ADHD Brain Symptoms: Signs to Look For
Recognizing ADHD brain symptoms is crucial for early intervention. Common symptoms include difficulty maintaining focus, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. These traits often interfere with daily tasks, making personalized strategies essential for those affected.
4. ADHD Brain vs Normal Brain Scan:
Brain scans have revealed significant differences in structure and activity. The ADHD_brain vs normal brain scan often shows reduced activity in the prefrontal cortex—responsible for executive functions like decision-making and focus. This reduced activity explains why individuals with ADHD struggle with attention and impulse control.
5. ADHD Brain vs. Normal Behavior in Adults:
While ADHD is often diagnosed in childhood, many individuals continue to experience symptoms into adulthood. Common adult ADHD symptoms include:
- Difficulty Focusing: Struggling to concentrate on tasks and easily getting distracted.
- Impulsivity: Acting without thinking, making hasty decisions, or interrupting others.
- Hyperactivity: Feeling restless, fidgety, or having trouble sitting still.
- Organizational Challenges: Struggling with time management, planning, and prioritizing tasks.
6. ADHD Brain Development and Age:
The developing brain of a child with ADHD may show differences in structure and function compared to neurotypical brains. These differences can impact a child’s ability to learn, pay attention, and control their behavior. However, with appropriate interventions and support, many individuals with ADHD can successfully manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives.
7. ADHD Brain vs. Autistic Brain:
While both ADHD and autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are neurodevelopmental conditions, they have distinct characteristics. Individuals with ADHD may struggle with social skills and impulsivity, but they typically do not exhibit the same level of social and communication deficits as those with autism.

Conclusion:
the ADHD brain vs regular brain differences are clear when examining brain scans, dopamine levels, and behavioral patterns. The ADHD_brain vs normal brain scan reveals significant structural differences, including reduced activity in the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for attention and impulse control. Additionally, ADHD_brain vs normal brain dopamine levels are typically lower, affecting focus, motivation, and emotional regulation.
When comparing ADHD vs normal behavior in adults, the differences become even more apparent, with ADHD adults often exhibiting impulsivity, forgetfulness, and restlessness. Recognizing these ADHD brain symptoms is crucial for identifying the disorder early and providing effective support.
FAQS:
How is an ADHD brain different from a normal brain?
An ADHD brain differs in several ways, including reduced activity in the prefrontal cortex, which affects attention, decision-making, and impulse control. This leads to difficulties with focus, organization, and self-regulation compared to a typical brain.
Why do ADHD brains work faster?
ADHD brains may process information quickly, especially when multitasking or switching between tasks, due to the brain’s heightened alertness and impulsivity. However, this speed can lead to distractions and difficulty maintaining focus on one task for long periods.
Are people with ADHD more successful?
People with ADHD can be highly successful, particularly in environments that embrace creativity, spontaneity, and adaptability. While they may face challenges, many thrive by using their unique strengths, such as problem-solving, risk-taking, and innovative thinking.
What makes people with ADHD happy?
People with ADHD often find happiness in activities that provide immediate rewards, stimulation, and variety. Engaging in creative projects, physical activities, or jobs that allow flexibility can help maintain their focus and keep them motivated.
External Resources:
ADHD Brain Scans Explained – NIH
ADHD Development Research – NIMH

Empowering parents to raise happy, confident kids. Get practical parenting tips and advice on our blog, Smart Parent Guides.
