Jaundice in newborns is a common condition where a baby’s skin and eyes take on a yellowish tint due to elevated bilirubin levels. This article covers essential information about newborn jaundice, including what causes it, how to recognize its symptoms, and effective treatment options. Understanding jaundice in newborns helps ensure the baby’s well-being. Additionally, if your baby is also experiencing colic , it’s important to consult with your pediatrician, as managing colic and jaundice together can support your baby’s overall health.
1. What Causes Jaundice in Newborns?
Jaundice newborn occurs when there is too much bilirubin in a baby’s bloodstream. Bilirubin is a yellow substance produced when red blood cells break down. Newborns often have a higher amount of bilirubin because their liver is still maturing and might not process it efficiently.
The common causes of jaundice in newborn infants include:
- Physiological Jaundice: Most common in healthy babies, this form appears between 24 and 72 hours after birth and resolves on its own in about a week.
- Breastfeeding Jaundice: This happens when the baby isn’t feeding well, leading to dehydration and elevated bilirubin levels.
- Pathological Jaundice: Caused by issues such as blood group incompatibility, infections, or enzyme deficiencies, this type may need medical treatment.
Understanding what causes jaundice in newborns helps identify the severity and necessary treatments.
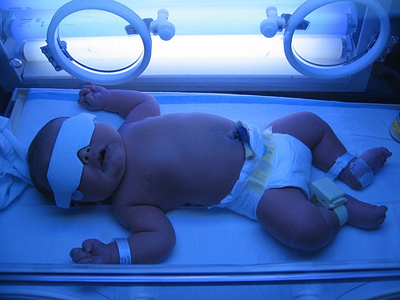
2. Symptoms of Jaundice in Newborns:
The primary symptom of newborn jaundice is yellowing of the skin and eyes. However, other signs can include:
- Yellowish skin (most noticeable on the face, chest, and belly).
- Yellow eyes: Bilirubin often accumulates in the whites of the eyes, making them appear yellow.
- Pale stools and dark urine: These can indicate high levels of bilirubin in the baby’s system.
- Poor feeding and lethargy: Babies with jaundice might be more tired and find it difficult to latch onto the breast or bottle.
If these symptoms appear in your baby, you may need to monitor bilirubin levels and contact your pediatrician.
3. Newborn Jaundice Treatment: What You Need to Know
Most cases of jaundice newborn are mild and resolve naturally. However, in more severe cases, treatment may be required. Treatment options for newborn jaundice include:
- Phototherapy (Light Therapy): The baby is placed under special blue lights that break down bilirubin in the skin. This is the most common treatment for moderate cases.
- Breastfeeding and Hydration: Frequent feedings help the baby pass bilirubin through stool and urine.
- Exchange Transfusion: In cases of severe high jaundice levels in newborns, where bilirubin reaches dangerously high levels, this procedure is used to replace some of the baby’s blood.
Understanding newborn jaundice treatment helps parents ensure their baby gets the right care in a timely manner.
4. When to Worry About Jaundice in Newborns:
Jaundice in newborns is usually not a cause for alarm unless the bilirubin levels rise too quickly or reach dangerously high levels. Here’s when you should be concerned:
- Jaundice appears within the first 24 hours: This could indicate an underlying condition.
- Jaundice lasts longer than two weeks: Persistent jaundice might require further investigation.
- Baby is lethargic or refusing to feed: This could signal a more serious form of jaundice.
If any of these occur, contact your healthcare provider immediately to assess your baby’s bilirubin levels and ensure appropriate intervention.
5. Signs of Recovery from Jaundice in Newborns:
As the body processes and eliminates excess bilirubin, you’ll notice signs that your baby is recovering from jaundice. These include:
- Improved skin color: The yellowish tint to the skin will gradually fade, typically starting from the face.
- Better feeding habits: Your baby will become more alert and eager to nurse.
- Normal urine and stool: The baby’s urine should lighten in color, and stools will become more yellow.

If you notice these changes, it’s a positive sign that the newborn jaundice is resolving.
6. How to Prevent Jaundice in Newborns:
While newborn jaundice is often unavoidable, you can take steps to help reduce the risk:
- Ensure frequent feeding: Babies who are breastfed or formula-fed should be fed regularly, especially in the first few days after birth.
- Monitor hydration: Adequate fluid intake helps the baby’s liver function properly and process bilirubin.
- Avoid dehydration: If your baby is not nursing effectively, consider consulting a lactation consultant.
While it’s difficult to completely prevent jaundice disease in newborns, taking these steps can help reduce the chances of complications.
7. Newborn Jaundice Levels: Understanding the Bilirubin Chart
Doctors often use a newborn jaundice level chart to determine the severity of jaundice based on the bilirubin level and the baby’s age in hours. Here’s a general idea of the bilirubin levels:
- Mild Jaundice: Bilirubin levels between 5 and 12 mg/dL.
- Moderate Jaundice: Bilirubin levels between 12 and 20 mg/dL.
- Severe Jaundice: Levels above 20 mg/dL, requiring immediate treatment.
Understanding newborn jaundice levels helps parents and healthcare providers determine whether medical intervention is necessary.

8. What is a Dangerous Level of Bilirubin in Newborns?
A dangerous level of bilirubin is typically considered to be above 20 mg/dL, though this can vary depending on the baby’s age and weight. If your baby’s bilirubin levels reach this point, they may require exchange transfusion to prevent serious complications like brain damage (kernicterus).
Conclusion:
Understanding newborn jaundice, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for every parent. Most cases are temporary and resolve without intervention, but knowing the signs of recovery and when to seek medical advice can help keep your baby safe.
By staying informed about the normal range of jaundice in newborns and newborn jaundice poop changes, you can provide the best care possible and ensure your baby’s healthy development.
FAQS:
What to do if a newborn baby has jaundice?
If your newborn has jaundice, it’s important to monitor their skin color and seek medical advice. The pediatrician may suggest phototherapy (light treatment) to reduce bilirubin levels, encourage frequent breastfeeding, and ensure the baby is hydrated. In more severe cases, a blood test may be needed to check bilirubin levels.
How long will jaundice last in a newborn?
Jaundice in newborns typically lasts about 1 to 2 weeks. It usually peaks on the second or third day after birth and then starts to improve as the baby’s liver matures and processes bilirubin more efficiently. However, some babies may have jaundice for longer, especially if breastfeeding jaundice is involved.
Why do newborns get jaundice?
Newborns often get jaundice because their liver is still immature and unable to process bilirubin efficiently. The breakdown of red blood cells produces bilirubin, and in newborns, the liver may take a few days to fully function. Other causes can include breastfeeding difficulties or blood group incompatibility.
How long is jaundice normal in a newborn?
Jaundice is usually normal for a newborn during the first week of life. Physiological jaundice, which is the most common form, typically resolves within 2 weeks. If jaundice persists beyond this time or appears severe, it should be evaluated by a doctor.
How do you treat jaundice in newborns?
Jaundice in newborns is commonly treated with phototherapy, where the baby is placed under special lights that help break down bilirubin. Frequent breastfeeding or formula feeding can also help lower bilirubin levels by promoting stool and urine production. In severe cases, an exchange transfusion may be needed.
Does breast milk help with jaundice?
Yes, breastfeeding can help with jaundice in newborns. Breast milk encourages frequent feedings, which helps the baby pass bilirubin through stool. However, in some cases, poor feeding or dehydration can worsen jaundice, so it’s important to ensure the baby is feeding properly and frequently.
Is 14 a high bilirubin level in newborns?
A bilirubin level of 14 mg/dL in a newborn is considered moderate. It is not typically dangerous but may require monitoring or mild treatment, such as phototherapy, especially if the baby is within the first few days of life. Higher levels may need more aggressive treatment, so it’s important to consult with a pediatrician for guidance.
External Resources:
Mayo Clinic – Jaundice in Newborns
- Overview of symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment for jaundice in newborns.
National Institutes of Health (NIH) – Jaundice in Newborns
- Insights into bilirubin levels, testing, and treatment methods.

Empowering parents to raise happy, confident kids. Get practical parenting tips and advice on our blog, Smart Parent Guides.
