Celiac disease is a serious autoimmune disorder that requires careful attention to celiac disease treatments, especially in celiac disease in children. Recognizing early disease symptoms in children is crucial for proper management.
This not only disrupts nutrient absorption but can also lead to deficiencies in essential micronutrients, which are crucial for a child’s growth and development. Left untreated, these deficiencies can cause various symptoms and long-term health issues. In this article, we’ll explore the key aspects of celiac disease, focusing on celiac_disease treatments for children, symptoms, diagnosis, and effective dietary management, including the importance of student meals that are both nutritious and gluten-free.
What is Celiac Disease?
Celiac disease is more than just a gluten intolerance; it’s an autoimmune disorder that can cause significant damage to the small intestine. When gluten is ingested, the immune system reacts aggressively, leading to inflammation and harm to the villi—tiny finger-like projections that line the small intestine and absorb nutrients. This damage can result in malnutrition and a variety of health problems, especially in children who are still growing.
Celiac Disease Symptoms in Children:
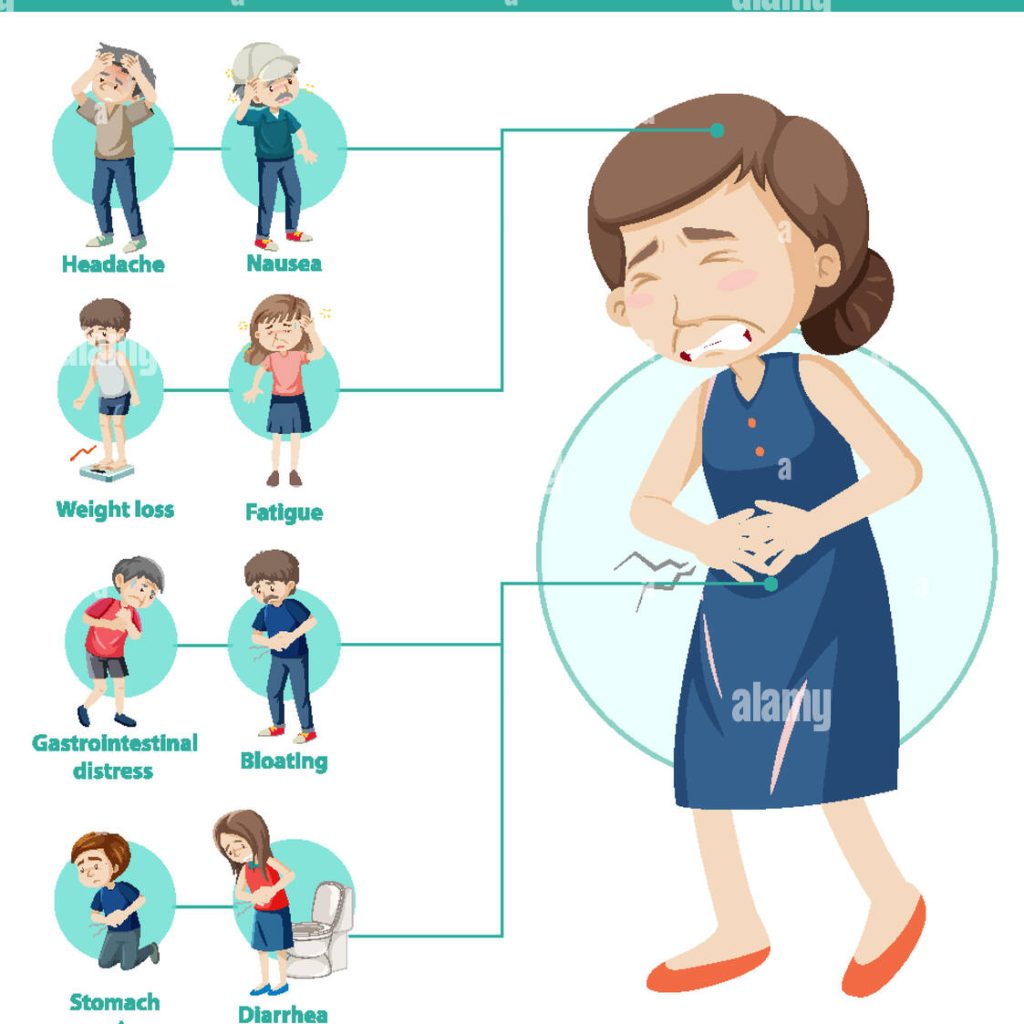
Recognizing celiac disease symptoms in children is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Symptoms can vary widely but often include:
- Digestive issues: Abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation are common.
- Behavioral changes: Irritability, mood swings, and difficulty concentrating may be observed.
- Growth problems: Children may experience delayed growth or weight loss despite eating regularly.
- Skin issues: Some children develop a gluten allergy rash called dermatitis herpetiformis, which is itchy and blistering.
- Other symptoms: Fatigue, hair loss, and anemia due to nutrient deficiencies are also possible.
Early recognition of these symptoms is vital to prevent long-term complications.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis: How to Diagnose Celiac Disease in a Child
Diagnosing celiac disease in children begins with a careful examination of symptoms followed by specific tests. A celiac disease blood test is often the first step, measuring the presence of certain antibodies that indicate an immune response to gluten. If the blood test is positive, a biopsy of the small intestine may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Celiac_disease serology involves testing the blood for various antibodies to help diagnose the condition. Early diagnosis is crucial for preventing further damage to the intestine and ensuring proper growth and development in children.
6 Effective Celiac Disease Treatments for Children:
The primary and most effective treatment is a strict, lifelong gluten-free diet. This means avoiding all foods that contain gluten, including wheat, barley, and rye. Gluten is a protein found in these grains that triggers an immune reaction in people with celiac disease, damaging the lining of their small intestine.
- Avoid gluten-containing foods: This includes bread, pasta, cakes, cookies, pizza, and many processed foods.
2. Read food labels carefully: Look for the words “gluten-free” on food labels.
3. Be mindful of cross-contamination: Avoid cooking or preparing food on surfaces that have come into contact with gluten-containing ingredients.
4. Nutritional supplements: In some cases, individuals with celiac disease may need nutritional supplements to address any deficiencies caused by malabsorption.
5. Medication for skin conditions: If you have dermatitis herpetiformis, a skin condition associated with celiac disease, your doctor may prescribe medication to help manage the rash.
6. Monitoring and follow-up: Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are important to monitor your progress, assess your nutrient status, and address any ongoing issues
Remember: Following a gluten-free diet is essential for managing celiac disease. With proper guidance and support, you can successfully navigate this dietary change and improve your overall health.
Celiac Disease Diet: Creating a Healthy, Gluten-Free Menu

Creating a balanced and nutritious diet is essential for managing the condition. Parents should focus on providing naturally gluten-free foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and gluten-free grains like rice and quinoa. A well-structured diet plan menu can help ensure that the child gets all the necessary nutrients without exposure to gluten.
It’s also important to be aware of cross-contamination, which can occur if gluten-free foods come into contact with gluten-containing products. Reading labels carefully and choosing certified gluten-free products can help prevent accidental gluten ingestion.
Clinical Features and Related Conditions:
Celiac disease clinical features can include a wide range of symptoms beyond just digestive issues. For instance, weight loss is a common problem due to poor nutrient absorption. Children may also experience hair loss as a result of vitamin deficiencies.
Another related condition is the gluten allergy rash, which affects some children. This rash, known as dermatitis herpetiformis, is intensely itchy and often appears on the elbows, knees, and buttocks. Proper treatment and a strict gluten-free diet can help manage these symptoms effectively.
The Role of a Celiac Disease Doctor: Monitoring and Support
Regular follow-ups with a celiac disease doctor are essential for monitoring the child’s health and ensuring that the gluten-free diet is being followed correctly. The doctor may order periodic celiac disease panel tests to check for antibodies and assess the effectiveness of the diet.
In cases where symptoms persist despite a gluten-free diet, additional treatments or dietary adjustments may be needed. Ongoing support from healthcare professionals can make a significant difference in managing celiac disease in child treatment.
Celiac Disease in Toddlers:
Managing celiac disease in toddlers presents unique challenges, especially when it comes to dietary restrictions. Symptoms such as changes in toddler poop, including diarrhea or constipation, and the development of a toddler rash may indicate celiac disease. Parents should work closely with a healthcare provider to create a treatment plan that meets their toddler’s specific needs.
Conclusion:
Celiac disease in children requires careful management, from recognizing symptoms to following a strict gluten-free diet. By understanding the clinical features, getting a proper diagnosis, and implementing effective treatments, parents can help their children lead healthy, symptom-free lives. If you suspect your child has this disease, consult with a healthcare provider to discuss the best steps for diagnosis and treatment.
FAQS:
What are the symptoms of silent celiac_disease?
Silent celiac disease may not have any noticeable symptoms, making it difficult to diagnose. However, some individuals may experience subtle signs like fatigue, anemia, or joint pain.
What are 5 signs and symptoms of celiac disease?
Five common signs and symptoms are abdominal pain, diarrhea or constipation, fatigue, weight loss, and anemia.
How does celiac affect a child?
It can affect a child’s growth, development, and overall well-being. It can lead to delayed growth, weight loss, irritability, and other behavioral changes.
How to diagnose celiac disease in a child?
Diagnosing this disease in a child typically involves a combination of blood tests and an intestinal biopsy.
- Blood Tests:
- Antibody testing: Blood tests are used to measure specific antibodies that are often elevated in people with celiac disease. These antibodies are produced in response to gluten.
- Common tests: Tissue transglutaminase IgA (tTG-IgA), deamidated gliadin peptide (DGP), and anti-endomysial antibodies (EMA) are frequently used.
- Intestinal Biopsy:
- Gold standard: An intestinal biopsy is considered the definitive test for this disease. It involves taking a small sample of tissue from the small intestine to examine for damage caused by gluten.
- Procedure: A gastroenterologist performs a procedure called endoscopy to obtain the biopsy.
Important Considerations:
- Gluten-containing diet: It’s essential for the child to be consuming a gluten-containing diet before the tests are performed. This is because the antibodies produced in response to gluten will be detectable in the blood.
- Family history: If there’s a family history of this disease or other autoimmune conditions, it can increase the likelihood of a diagnosis.
- Other symptoms: While blood tests and biopsy are the primary diagnostic tools, it’s also important to consider other symptoms the child may be experiencing, such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, or delayed growth.
If you suspect your child may have this disease, it’s recommended to consult with a pediatrician or gastroenterologist for a proper evaluation and diagnosis.
External Resources:
Celiac Disease Foundation: https://celiac.org/
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK):https://www.niddk.nih.gov/
Mayo Clinic:https://www.mayoclinic.org/
The Gluten Intolerance Group:https://gluten.org/

Empowering parents to raise happy, confident kids. Get practical parenting tips and advice on our blog, Smart Parent Guides.
